In planning a large bakery, choosing the energy type for the rotary oven is a critical decision.
Gas and electricity are the two primary energy forms on the market, each possessing its unique advantages and disadvantages. However, their initial investment, operational efficiency, and long-term costs vary.
This article provides a comprehensive comparison guide to help you make the best choice based on your actual operational needs.
I. Performance and Efficiency Comparison
| Feature | Gas Rotary Oven | Electric Rotary Oven |
| Heating Speed | Extremely fast. High calorific value of gas combustion allows it to rapidly reach the required temperature and recover quickly. | Slower. Heating speed depends on the power and number of electric heating elements. |
| Heat Distribution | Relies on heat exchanger design. Uniformity depends on the fan and air duct system. | Good. Heat distribution is easily controlled through the precise arrangement of electric heating tubes. |
| Baking Cost | Generally lower. In most regions, the price per unit of calorific value for natural gas is lower than electricity. | Generally higher. Costs increase significantly, especially during peak electricity hours. |
| Installation Requirements | Requires installation of gas pipelines, a chimney, and additional safety exhaust systems. | Only requires sufficient electrical capacity access; installation is relatively simple. |
II. Initial Investment and Installation Costs
1. Gas Oven: Higher Upfront Installation Investment
The installation and infrastructure costs for a gas oven are often higher:
Gas Access: Requires professional laying of gas pipelines.
Flue System: Gas combustion produces exhaust gases, necessitating the installation of code-compliant, high-temperature resistant flues and ventilation systems.
Safety Requirements: Gas equipment has stricter safety requirements, requiring additional gas leak monitoring and fire suppression facilities.
2. Electric Oven: Simpler Installation, but Power Capacity Expansion Must Be Considered
Electric ovens have fewer installation steps and do not require complex flue systems. However, their biggest cost risk lies in the power capacity:
Power Load: Commercial rotary ovens typically have power ratings ranging from $40\text{kW}$ to over 100kW.
III. Long-Term Operational Cost Analysis (ROI)
The key factor determining the choice of energy is the long-term operational cost, or Return on Investment (ROI).
1. Fuel Cost: Regional Differences Must Be Considered
In most regions, the unit heat value cost of natural gas is significantly lower than electricity. For central kitchens operating long hours and high frequency daily, the fuel cost savings from a gas oven over several years can easily offset the initial installation costs.
Key Reminder: Before making a decision, be sure to consult local commercial natural gas prices and commercial electricity peak and off-peak tariffs.
Taking the Nicko 12/16/32/64 Trays Rotary Oven as an example, it uses an advanced Japanese electronic burner to ensure fuel is fully combusted, maximizing the efficiency of converting heat into baking energy, thereby reducing gas consumption.
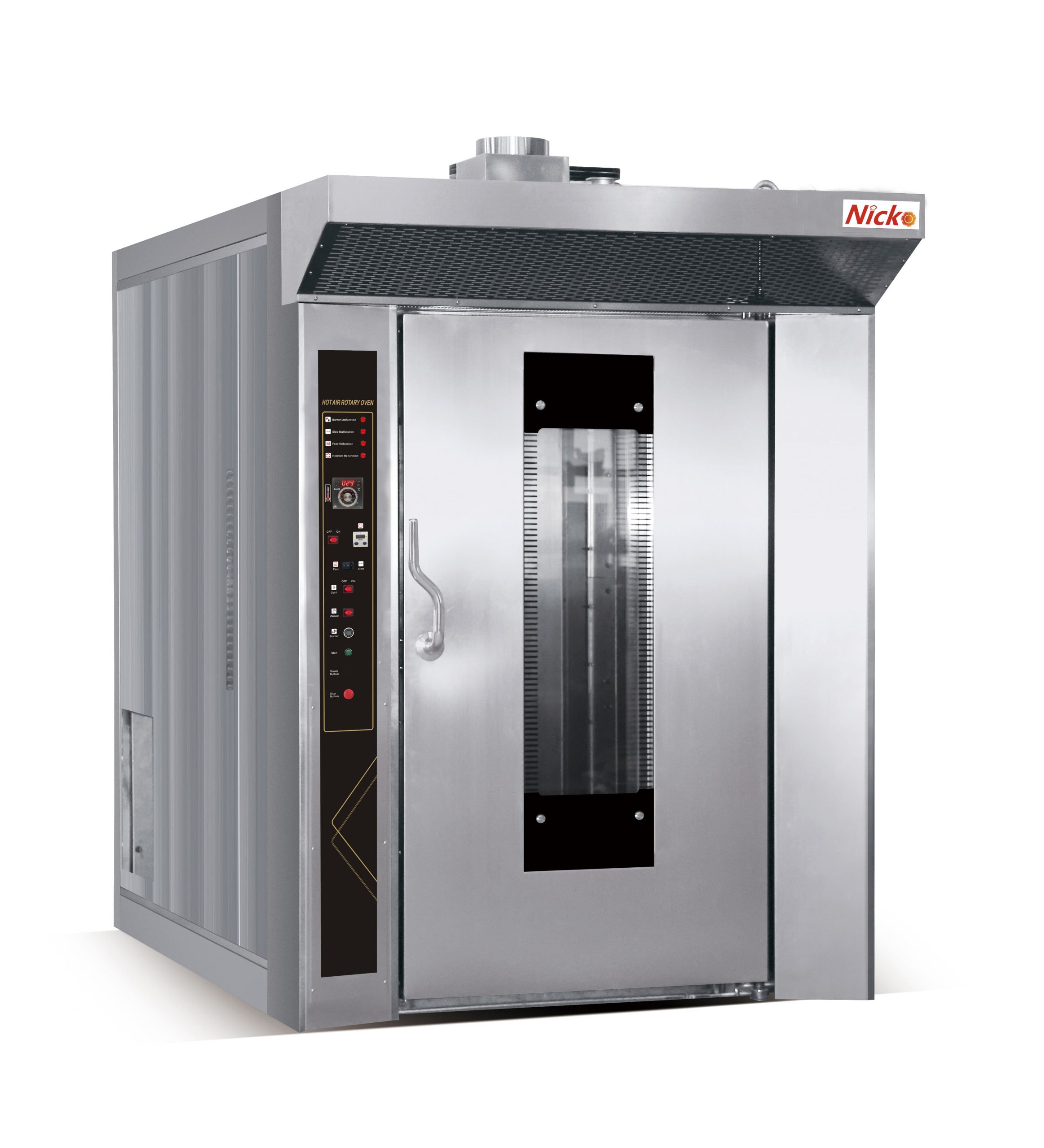

Additionally, this product uses high-temperature rock wool with a density up to $120\text{K}$, resistant to temperatures up to 800C. This reduces heat loss to the exterior, minimizing the operating frequency and time of the heater or burner, and significantly lowering energy consumption.
2. Maintenance Costs
Gas Oven: Maintenance is relatively complex, requiring regular inspection and cleaning of the gas burner, heat exchanger, and flue to ensure safety and efficiency.
Electric Oven: Maintenance is typically simpler, primarily focusing on the lifespan of the electric heating elements and contactors.
Taking the Nicko 12/16/32/64 Trays Rotary Oven as an example, its features include “Original Schneider Relays and Japanese Imported Burners,” which have a longer service life, reducing replacement frequency.
Furthermore, its internal structure incorporates $10\text{-}15\text{mm}$ thick fire arrester castings to protect the combustion chamber from burnout, leaks, and deformation, extending the service life of the combustion chamber. Its internal and external materials are made of stainless steel, offering corrosion resistance and easy cleaning, thus lowering maintenance needs caused by corrosion.
3. Thermal Efficiency: The Advantage of Gas Ovens
Excellent gas rotary ovens, through efficient Heat Exchanger designs, maximize the transfer of heat from gas combustion to the oven air. Their thermal efficiency is often very high, further solidifying their advantage in operational costs.
Taking the Nicko 12/16/32/64 Trays Rotary Oven as an example, it is equipped with a customized intelligent computer control panel and solid-state resistance relays, providing more precise temperature control. This means the oven avoids unnecessary overheating or temperature surges, preventing energy waste.
Moreover, it features a high-density sealed heat-lock design combined with high-temperature resistant double-tempered glass insulation, minimizing heat loss from opening the door and from the cabinet itself.
IV. Decision Guide: Choose Based on Your Needs
Before making a decision, it is recommended to request a detailed five-year operational cost projection report from your supplier or engineering contractor, comparing the input and output of different energy types in your local area to make the most economical and reliable commercial decision.
If you need to purchase a professional commercial oven, you are welcome to visit Nicko’s oven dedicated page. Both their gas and electric ovens are comprehensive, ensuring reliable quality at a competitive price: https://www.nicko.com.cn/products/oven/